Article Title :
Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones using AHP and Geospatial Techniques in Western Part of Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India 
3 (2019)
60-71
AHP , GIS , Groundwater Potential Zone , Cuddapah Basin , Groundwater , Remote Sensing


Present study is carried out for delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones (GWPZ) in Western part of Cuddapah basin, Southern India using Remote Sensing (RS), Geographical Information System (GIS) and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP). Various categorized thematic maps: geology, geomorphology (GM), slope, soils, lineament density (LD), drainage density (DD) and water levels fluctuations (WLF) were used for mapping and delineation of GWPZs. Suitable and normalized weights were assigned based on AHP to identify GWPZ. The GWPZ map was categorized into five GWPZs types: very poor, poor, moderate, good and very good. About 1.48% (6.05 km2) area is classified in ‘very good’, 25.95% (106.07 km2) in ‘good’, 47.11% (192.53 km2) in ‘moderate’, 22.12% (90.38 km2) in ‘poor’ and 3.34% (13.66 km2) in ‘very poor’ category. The acquired outcomes were validated with water levels fluctuations in pre- and post-monsoon seasons. GIS-based multi-criteria decision making approach is useful for preparation of precise and reliable data. The AHP approach, with the aptitudes of the geospatial data, various data bases can be combined to create conceptual model for identification and estimation of GWPZs.
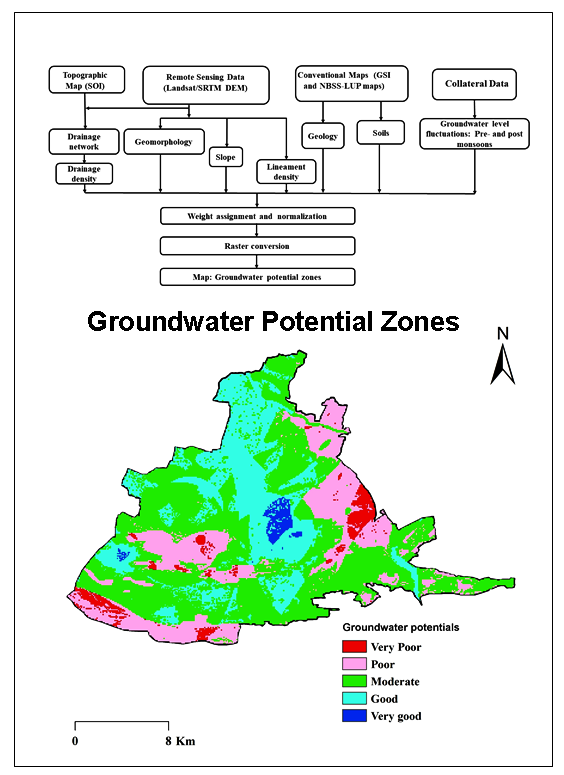
The groundwater levels are declining at a rapidly in some parts of southern India.
Remote Sensing, GIS and AHP techniques were used to delineate the groundwater potential zones (GWPZ).
Weightages were assigned for different thematic maps to obtain GWPZs.
Results are useful for decision and planning for sustainable groundwater management.
Kumar, B. P., Babu, K. R., Rajasekhar, M., and Ramachandra, M., 2019. Assessment of land degradation and desertification due to migration of sand and sand dunes in Beluguppa Mandal of Anantapur district (AP, India), using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J. Ind. Geophys. Union, 23(2), 173-180.
Nagaraja Rao, B. K., Rajurkar, S. T., Ramalingaswamy, G. and Ravindra Babu, B., 1987. Stratigraphy, structure and evolution of the Cuddapah basin. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, 6, 33-86.
Rajasekhar, M., Gadhiraju, S. R., Kadam, A. and Bhagat, V., 2020. Identification of groundwater recharge-based potential rainwater harvesting sites for sustainable development of a semiarid region of southern India using geospatial, AHP, and SCS-CN approach. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(2), 24.
Ramachandra, M., Raghu Babu, K., Rajasekhar, M., Pradeep Kumar, B., 2019. Lineament analysis by Remote Sensing and GIS techniques for groundwater and mineral exploration in and around Lingala and Pendlimarri Mandal's of Kadapa District, A. P, India. SRG International Journal of Geoinformatics and Geological Science (SSRG-IJGGS), 6(2), 38-44.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Saaty, T. L., 1999. Fundamentals of the analytic network process. International Symposium of the Analytic Hierarchy Process (ISAHP), Kobe, Japan.
Zeinolabedinia, M. and Esmaeilyb, A., 2015. Groundwater potential assessment using geographic information. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 1, W5.