Article Title :
Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Geospatial Techniques and WQI in North East of Adama Town, Oromia Region, Ethiopia
3 (2019)
22-36
Ethiopia , Groundwater , GIS , Water Quality Index , Spatial Interpolation


Assessment of groundwater quality is vital for the sustainable use of the resources for domestic and agricultural purposes. In this study spatial variation of physicochemical parameters were analyzed for Northeast Adama Town. Water Quality Index (WQI) and irrigation indices were used to determine the suitability of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes, respectively. Further, the physical-chemical results were compared with the Ethiopian standards and the World Health Organization (WHO) standards for drinking and public health. Using GIS interpolation methods in Arc GIS 10.3.1, spatial distribution maps of pH, TDS, EC, Cl−, HCO32−, SO42−, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+, RSC, SAR, Na% were prepared. Results indicated that except ASTU well 2, all samples are below the desirable limits of WHO. The WQI results indicated that 85% of samples and 15% of samples were in good and poor categories, respectively. Irrigation indices show that most groundwater samples have excellent water classes, indicating that they are suitable for irrigation purposes.
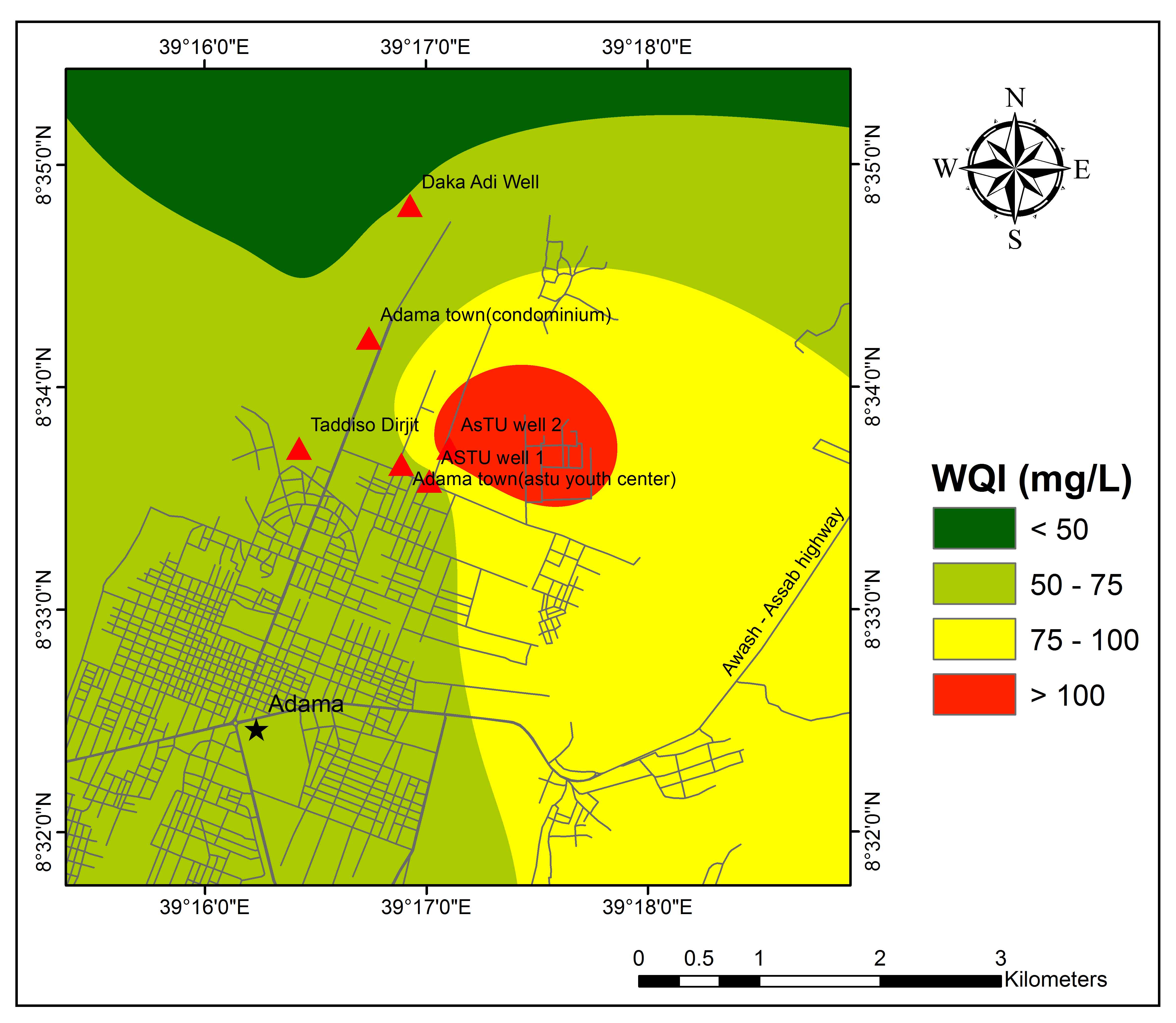
Groundwater samples were analysed to understand the concentration of major cation and anions.
Groundwater quality was analysed for drinking and irrigation purposes using WQI.
WQI ranges between good to poor category for majority of the samples.
The most of the groundwater samples are excellent and suitable for irrigation purposes.
Altchenko, Y., Awulachew, S.B., Brida, A.B., Diallo, H.A., Mogbante, D., Pavelic, P., Tindimugaya, C. and Villholth, K.G., 2011. Management of groundwater in Africa including transboundary aquifers: implications for food security, livelihood and climate change adaptation. African climate policy centre working paper 6. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: U. Nations Econ. Comm. for Africa (UNECA).
APHA, 1995. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th Ed. American public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Aravindan, S., Manivel, M., Rajendran. S., Bhuvaneshwari and Shankar, K., 2008. Groundwater investigations in the hard rock region of gadilam river basin, Tamil Nadu, Journal of Eco-chronicle, 3(1), 21-30.
Aravindan, S. and Shankar. K., 2011b. Groundwater quality in Paravanar River sub-basin, Cuddalore District, Tamilnadu, India, Gondwana Geological Magazine, 26(2), 139 - 146.
Aravindan, S., Shankar, K., Poovalinga Ganesh, B. and Dharani Rajan, K., 2010. Groundwater geochemical mapping of in the hard rock area of Gadilam River basin, using GIS technique, Tamil Nadu, Indian Journal of Applied Geochemistry, 12(2), 209-216.
Assegide, G., 2007. Geology of Addis Ababa city (NC 37-10/ X and Y and NC 476/ E and Sub sheets, Geological Survey of Ethiopia, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Ayenew, T., 2005. Major ions composition of the groundwater and surface water systems and their geological and geochemical controls in the Ethiopian volcanic terrain. SINET, Ethiopian J. Sci. 28 (2), 171-188.
Berehanu, B., 2007. Impact of industries and urbanization on water resource in Modjo river catchment. Unpublished M.Sc. Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Chernet, T., 1982. Hydrogeology of the Lakes Region, Ethiopia. Ministry of Mines and Energy, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Davis, S. N. and Dewiest, R. J. M., 1966. Hydrogeology, Willey, New York, 463.
Farooq, G. and Ustad, I., 2015. Investigation of physico-chemical properties of groundwater from Commercial Boreholes in Altamash Colony, Aurangabad. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 4, 1625-1630.
Gebrehiwot, A. B., Tadesse, N. and Jigar, E., 2011. Application of water quality index to assess suitability of groundwater quality for drinking purposes in Hantebet watershed. Tigray, Northern Ethiopia, ISABB Journal of Food and Agriculture Science, 1, 22-30.
Gizaw, B., 2002. Hydrochemical and Environmental Investigation of the Addis Ababa Region, Ethiopia. PhD Thesis, Ludwig- Maximilians-University of Munich, Germany, 157.
Haile G., 1999. Hydrogeochemistry of waters in Lake Ziway area. Paper presented at the 25th WEDC Conference on Integrated Development for Water Supply and Sanitati, 286-189.
Halcrow, 1989. Rift valley lakes integrated natural resources development master plan. Ethiopian Valleys Development Studies Authority. Unpublished report.
Hem, J. D., 1985. Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, USGS water supply paper, 2254, 117-120.
Jhariya, D. C., Kumar, T., Dewangan, R., Dharm Pal. and Dewangan, P. K., 2017. Assessment of groundwater quality index for drinking purpose in the Durg district, Chhattisgarh using Geographical Information System (GIS) and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) techniques. J Geol Soc India. 89, 453.
Kalra, Y. P. and Maynard, D. G., 1991. Methods manual for forest soil and plant analysis. Information report NOR-X-319, Northwest Region, Northern Forestry Centre, Forestry Canada.
Kumar, P. S. and Balamurugan, P., 2018. Evaluation of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose in Attur Taluk, Salem, Tamilnadu, India. Water and Energy International, 61(4), 59-64.
Li, P., Qian, H. and Wu, J., 2011. Groundwater suitability for drinking and agricultural usage in Yinchuan Area, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci., 1, 1241-1249.
Mohr, P. A., 1967. The Ethiopian rift system. Bulletin. Geophysical Observatory. Addis Ababa, 268.
Raghunath, H. M., 1987. Ground water: Hydrogeology, ground water survey and pumping tests, rural water supply and irrigation systems. New Age International (P) Ltd. Publishers.
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S., 2011c. Assessment of Ground Water Quality in Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2 (5), 92-103.
Shankar, K, Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S., 2011a. Spatial distribution of groundwater quality in Paravanar river sub basin, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 1(4), 914-931.
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S., Rajendran, S., 2010. GIS based groundwater quality mapping in Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 1(3), 282-296.
Singh, D. F., 1992. Studies on the water quality index of some major rivers of Pune, Maharashtra. Proceedings of the Academy of Environmental Biology, 1(1), 61-66.
Singh, P., Khan, I., 2011. Ground water quality assessment of Dhankawadi ward of Pune by using GIS. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 2, 688-703.
Subba Rao, N., 1997. Studies on water quality index in hard rock terrain of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. National Seminar on Hydrology of Precambrian Terrains and hard rock areas, 129-134.
Todd, D. K., 1980. Ground Water Hydrology - John Wiley & Sons, New York, 535.
UNDP, 1973. Geology, geochemistry and hydrology of hot springs of the East African Rift system within Ethiopia. UNDP report DD/SF/ON-11, UNDP, New York, 300.
Venkateswaran, S., Karuppannan, S. and Shankar, K., 2012. Groundwater quality in Pambar Sub-Basin, Tamil Nadu, India Using GIS. International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 3(10), 82- 787.
Wagh, V. M., Panaskar, D. B., Varade, A. M., Mukate, S. V., Gaikwad, S. K., Pawar, R. S., Muley A. A. and Aamalawar, M. L., 2016. Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of the groundwater resources of Nanded tehsil, a part of southeast Deccan Volcanic Province, Maharashtra, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(21), 1418.
WHO [World Health Organization], 2011. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed., Geneva, Switzerland.
Wilcox, L.V., 1955. Classification and use of irrigation waters. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Circ, Washington, DC, 969.